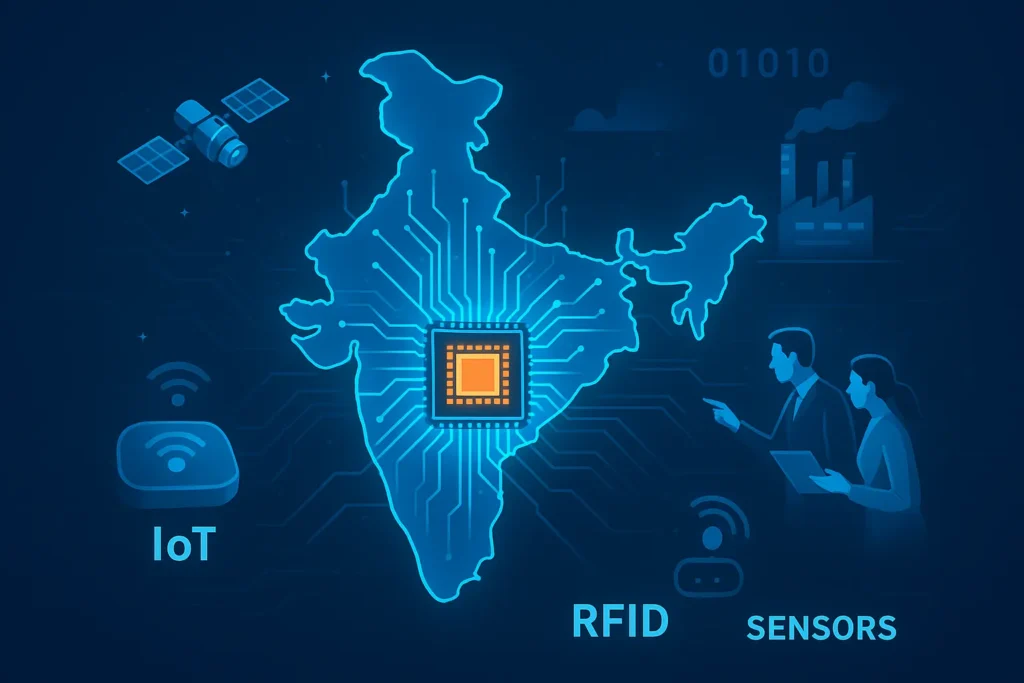
India has achieved a historic milestone with the launch of its first 100% indigenous semiconductor chip in semicon 2025,designed and manufactured on home soil. This chip is set to power IoT devices, RFID tags, and sensor systems—a breakthrough moment for a country that has long relied on semiconductor imports.
This step marks the beginning of India’s serious entry into the global semiconductor race, with implications for technology, economics, and MSME opportunities.
India’s Semiconductor Journey
Early Steps (1960s–1980s)
- Bharat Electronics Limited (BEL) started semiconductor manufacturing in the 1960s.
- In 1984, the Semi-Conductor Laboratory (SCL) in Mohali was set up, contributing chips even to ISRO’s space missions.
Lost Opportunities (1990s–2000s)
- Lack of infrastructure and policy consistency kept India behind while Taiwan’s TSMC and Korea’s Samsung became global leaders.
The Revival (2021–present)
- The Indian government launched the Semiconductor Mission with a ₹76,000 crore package.
- New fabs, testing units, and design incentives were rolled out.
- The launch of the first indigenous chip shows India’s potential to build its own ecosystem.
Where Are Semiconductors Used?
Semiconductors are the brains of modern electronics. Their applications include:
- Consumer electronics – smartphones, laptops, wearables
- Automotive – electric vehicles (EVs), advanced driver systems
- Industrial & healthcare – automation, robotics, diagnostics
- Defense & aerospace – satellites, communication systems
- Smart cities – IoT sensors, RFID-based logistics
India vs Global Semiconductors Leaders
| Factor | India (Emerging) | Global Leaders (Taiwan, Korea, USA) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Level | 28nm–90nm mature nodes | 3nm–5nm cutting-edge |
| Market Share | <1% | TSMC + Samsung control >50% |
| Strengths | Chip design, IoT, automotive applications | Advanced fabs, AI & HPC chips |
| Ecosystem | Growing, supported by MSMEs & startups | Mature, globally dominant |
India is starting with mature-node chips for IoT and automotive—industries with massive growth potential.
Economic Benefits of Semiconductors Manufacturing in India
- Reduced imports – Lower dependence on Taiwan and China.
- Job creation – Each fab can generate 20,000+ jobs.
- Export growth – India can tap into the US$600+ billion global semiconductor market.
- Supply chain resilience – Critical for national security and strategic autonomy.
India’s semiconductors market is projected to grow from US$34 billion in 2023 to over US$100 billion by 2032.
MSMEs in India’s Semiconductors Business
Can MSMEs Manufacture Chips?
Building fabs requires billions of dollars, so MSMEs usually don’t set up fabs. But they play a key role in design, testing, packaging, and services.
MSME Incentives
The Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) Scheme offers up to ₹15 crore support for MSMEs working on chip design and prototyping.
Emerging Indian Semiconductors Companies
- Sankalp Semiconductors – Global leader in chip design.
- MosChip Technologies – Fabless semiconductor company focusing on IoT.
- Semtronics MicroSystems – Specializes in automotive and communication IC design.
- SPEL Semiconductors – India’s only assembly and testing service provider.
- Tata Elxsi, Vedanta, HCL, Dixon Technologies – Larger players investing heavily in semiconductors growth.
Conclusion: India’s Silicon Future
The launch of India’s first indigenous semiconductors chip is more than a technical milestone—it’s a turning point.
- For the nation, it reduces dependence on imports and strengthens supply chains.
- For the economy, it promises jobs, exports, and innovation.
- For MSMEs and startups, it opens doors in design, testing, and packaging.
India has finally entered the global chip race—not just as a buyer, but as a builder.
FAQ: India’s Semiconductors Industry
Q1: What is India’s first indigenous semiconductors chip used for?
It is designed for IoT devices, RFID tags, and sensor systems.
Q2: Why are semiconductors important?
Semiconductors power almost all modern devices, from smartphones and EVs to satellites and medical equipment.
Q3: Who are the global leaders in semiconductors manufacturing?
Taiwan (TSMC), South Korea (Samsung), and the USA (Intel, Nvidia, Qualcomm) are the current global leaders.
Q4: Can MSMEs enter semiconductor manufacturing in India?
Full-scale fabs are too costly, but MSMEs are entering through chip design, testing, packaging, and fabless startups.
Q5: What government schemes support the semiconductor industry?
The Semiconductor Mission with ₹76,000 crore incentives and the Design-Linked Incentive (DLI) scheme for startups/MSMEs.
Q6: How big is the semiconductor market in India?
It is valued at US$34 billion (2023) and projected to cross US$100 billion by 2032.